Split Population Logit
Download ado files and code for predicted probabilities/first differences.
In many circumstances political scientists study binary dependent variables that have been measured with bias. For example, in surveys the strategic interests of actors can lead them to misrepresent an attitude or behavior to the surveyor in a non-random fashion. Data on terror or torture that are coded using media reports likely suffer from a similar bias related to factors such as freedom of the press in a country.
We, Jacqueline DeMeritt, Wonjae Hwang, Will Moore, and Andy Beger, have adapted and implemented a split population logit model in Stata to deal with those issues.
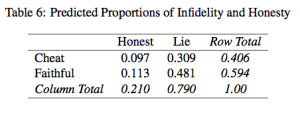
To give you an idea of what this new model allows one to do, consider the issue of self-reported infidelity between romantic partners. Using survey data, the reported rate of infidelity is about 13% of the sample. Yet common sense would suggest that this rate be higher, at least due to social desirability bias that would lead respondents who did in fact cheat lie about it to avoid the negative stigma. The split population logit model allows us to separate respondents’ rates of honesty and infidelity separately, as shown in the table excerpt from our paper. It shows for example that 41% of the sample likely cheated on their partner, but also that around three-quarters chose to lie about it when surveyed. Quite a difference from the 13% reported in the observed data.
The split population logit is implemented in Stata using these ado files. Here are also do files that calculate first differences and predicted probabilities.
Here are replication files for the simulations we used to evaluate our estimator and replication files for the infidelity example. The simulations were run through Florida State University High Performance Computing.
Paper to follow in a few weeks.